Complete Guide to Finance Reconciliation in 2024
Introduction to Financial Reconciliation
Finance reconciliation is a systematic process that involves comparing financial records, such as transactions, accounts, and statements, to ensure accuracy, consistency, and integrity in a company's financial data. It serves as a crucial component of financial management, providing insights into the financial health of an organisation and aiding in decision-making processes.
In this guide, we'll cover the intricacies of finance reconciliation, from methods and challenges to best practices. We'll explore why finance reconciliation is essential for businesses of all sizes and industries, highlighting its role in maintaining financial integrity and facilitating informed decision-making. Additionally, we'll get into the benefits of automating the finance reconciliation process with tools like Nanonets, which streamline finance reconciliation workflows and help organisations drive growth.
Whether you're a finance professional looking to enhance your reconciliation practices or a business owner seeking to streamline your financial processes, this article will provide practical insights and tips on navigating finance reconciliation.
What is Finance Reconciliation?
Finance reconciliation is the process of meticulously comparing two sets of financial records to validate the accuracy and consistency of financial data. It involves verifying that transactions recorded in an organisation's accounting system align with supporting documentation, such as bank statements, invoices, receipts, and other financial documents. The ultimate goal of finance reconciliation is to ensure that all financial transactions are accurately recorded and accounted for in the organisation's books.
At its core, finance reconciliation serves as a critical control mechanism to safeguard against errors, discrepancies, and fraudulent activities in financial reporting. By reconciling financial records, businesses can identify and rectify any inconsistencies promptly, thereby maintaining the integrity and reliability of their financial data.
Financial reconciliation encompasses various types, including bank reconciliation, account reconciliation, invoice reconciliation, and balance sheet reconciliation, each serving specific purposes in the financial management process. For instance, bank reconciliation involves comparing a company's bank statement with its internal records to ensure that all transactions, deposits, and withdrawals are accurately reflected and accounted for. Similarly, account reconciliation involves reconciling individual accounts, such as accounts payable and accounts receivable, to verify outstanding balances and ensure completeness and accuracy.
In the next section, we discuss why finance reconciliation is important for businesses.
The Importance of Financial Reconciliation
The process of reconciling financial statements serves multiple critical purposes within an organization. Finance reconciliation ensures the accuracy and integrity of financial records by verifying the consistency and completeness of transactions. By identifying and rectifying errors or discrepancies promptly, businesses can maintain reliable financial data for decision-making and reporting purposes.
Finance reconciliation also helps businesses comply with regulatory standards and reporting requirements imposed by government authorities and regulatory bodies. By reconciling financial records, businesses can ensure adherence to accounting principles, standards, and regulations, thereby minimizing the risk of non-compliance and potential penalties.
It also serves as a vital tool for detecting errors, discrepancies, and fraudulent activities in financial transactions. By comparing financial records with supporting documentation, businesses can identify anomalies, irregularities, or unauthorized transactions that may indicate fraudulent behavior or internal control weaknesses.
Accurate and reliable financial data is essential for informed decision-making at all levels of an organization. Finance reconciliation provides decision-makers with confidence in the accuracy and completeness of financial information, enabling them to make strategic, data-driven decisions that drive business growth and profitability.
Effective finance reconciliation processes promote operational efficiency by streamlining financial reporting, reducing errors, and minimizing manual intervention. By automating repetitive reconciliation tasks and leveraging technology solutions, businesses can improve efficiency, reduce costs, and reallocate resources to value-added activities.
In summary, finance reconciliation is a fundamental practice that underpins effective financial management and reporting. By ensuring the accuracy, integrity, and reliability of financial data, businesses can maintain compliance, mitigate risks, support decision-making, and drive operational efficiency, ultimately contributing to long-term success and sustainability.
Different Types of Financial Reconciliation
Financial reconciliation encompasses various types, each serving specific purposes in the financial management process.
Bank reconciliation is the process of comparing an organization's internal financial records, such as cash transactions, deposits, and withdrawals, with its bank statement. The goal is to ensure that the balances in the organization's accounting system match those in its bank records. Discrepancies may arise due to outstanding checks, bank fees, interest charges, or errors in recording transactions. Bank reconciliation helps businesses identify and rectify these discrepancies, ensuring the accuracy of their cash balances.
Balance sheet reconciliation involves comparing the balances of various accounts on the balance sheet, such as assets, liabilities, and equity, with supporting documentation and source data. The objective is to ensure that all transactions are accurately recorded and classified, and that the balance sheet reflects the true financial position of the organization. Balance sheet reconciliation helps businesses identify errors, omissions, and misclassifications in financial reporting, ensuring compliance with accounting standards and regulatory requirements.
Intercompany reconciliation involves reconciling transactions and balances between different entities or divisions within the same organization. It ensures that intercompany transactions, such as intercompany sales, purchases, loans, and transfers, are properly recorded and eliminated to prevent double counting or misstatements in financial reporting. Intercompany reconciliation helps businesses consolidate financial statements accurately and assess the financial performance of individual entities or divisions within the organization.
Revenue reconciliation focuses on verifying the accuracy and completeness of revenue transactions recorded in the organization's financial records. It involves comparing revenue recognized in the accounting system with supporting documentation, such as sales invoices, contracts, and revenue schedules. Revenue reconciliation helps businesses ensure that all revenue streams are properly accounted for, revenue recognition criteria are met, and any discrepancies or irregularities are identified and addressed.
Expense reconciliation involves verifying the accuracy and completeness of expense transactions recorded in the organization's financial records. It includes comparing expenses incurred, such as purchases, operating expenses, and overhead costs, with supporting documentation, such as invoices, receipts, and expense reports. Expense reconciliation helps businesses control costs, identify discrepancies or unauthorized expenses, and ensure compliance with budgetary constraints and spending policies.
Challenges in Financial Reconciliation
Financial reconciliation is a crucial process for ensuring the accuracy and integrity of an organization's financial data. But it often comes with its own set of challenges that can, if not handled properly, can impede efficiency, accuracy, and a company’s financial integrity.
Some common challenges in financial reconciliation include:
- Data Inaccuracies: One of the primary challenges in financial reconciliation is dealing with data inaccuracies. Errors in recording transactions, missing entries, or discrepancies between internal records and external sources can lead to inaccuracies in financial statements. These inaccuracies can arise from manual data entry errors, system glitches, or inconsistencies in data sources. Resolving data inaccuracies requires meticulous review and analysis of financial records, which can be time-consuming and resource-intensive.
- Time-Consuming Process: Financial reconciliation is often a time-consuming process, particularly for organizations with large volumes of transactions or complex financial structures. Reconciling multiple accounts, verifying transactions, and investigating discrepancies require significant time and effort from finance teams. Moreover, the manual nature of many reconciliation tasks can further contribute to delays in the reconciliation process, impacting timely financial reporting and decision-making.
- Lack of Proper Documentation: Proper documentation is essential for conducting effective financial reconciliation. However, many organizations struggle with inadequate or incomplete documentation, making it challenging to verify transactions and reconcile accounts accurately. Missing invoices, receipts, or supporting documentation can hinder the reconciliation process and increase the risk of errors or discrepancies going unnoticed. Implementing robust documentation practices and document management systems can help address this challenge and ensure that all relevant information is readily available for reconciliation purposes.
- Complex Financial Structures: Organizations with complex financial structures, such as multinational corporations or conglomerates, face unique challenges in financial reconciliation. Intercompany transactions, diverse business units, and varying accounting standards across jurisdictions can complicate the reconciliation process and increase the risk of errors or misstatements. Coordinating reconciliation efforts across multiple entities or divisions and aligning accounting practices can be challenging, requiring careful coordination and communication among finance teams.
Addressing these challenges requires a proactive approach to financial reconciliation, leveraging technology solutions, implementing robust controls and processes, and investing in employee training and development. By overcoming these challenges, organizations can enhance the accuracy, reliability, and efficiency of their financial reconciliation processes, ultimately supporting informed decision-making and regulatory compliance.
In the next section, we outline how to perform financial reconciliation step-by-step.
Step-by-Step Guide to Financial Reconciliation
The process of reconciling finances and accounts, whether performed manually or automatically, follows a set of clear steps to ensure accuracy and integrity. Here’s a comprehensive guide:
Step 1: Consolidate
To start reconciling accounts, gather all relevant records, invoices, and ledgers related to the specific account type you're working on. For instance, monthly transactions like purchases, payments, expenses, and earnings have their sources. Collect these transaction sources in a single location.
Step 2: Compare
Afterward, compare transactions in your internal ledger with those in your bank statement or financial documents. This side-by-side review helps spot discrepancies and inconsistencies requiring attention.
Step 3: Identify
Here, you pinpoint payments in the internal cash register missing from the bank statement. These are often cash transactions not yet processed by the bank. Also, check deposits might have a delay in showing up. By recognizing these, you can adjust the bank statement for timing differences causing discrepancies.
Step 4: Confirm
After spotting adjustments, it's vital to log them correctly. If cash register receipts are absent in the bank statement, include them, and vice versa. The aim is to harmonize cash transactions between your internal ledger and the bank statement.
Step 5: Find errors
While uncommon, bank errors like duplicates, wrong transactions, or calculation mistakes can happen. To ensure precise reconciliation, thoroughly check the bank statement for such errors. If any differences are found, promptly inform the bank with the necessary details for correction.
Step 6: Balance records
After addressing discrepancies and fixing errors, the subsequent task is to guarantee balanced and accurate records. This entails reviewing the reconciled data and confirming that adjusted numbers match the overall financial status.
Financial Reconciliation: Best Practices
Adhering to established best practices in financial reconciliation is paramount for ensuring accuracy and efficiency in financial reporting. Here are key practices to consider:
- Ensure Accuracy with Internal Controls: A robust internal control system is vital for accurately documenting transaction records. This involves clearly defining the records to be captured and identifying necessary source documents for comparison. Automation solutions can streamline this process, incorporating approval workflows that specify required information for transactions, such as reimbursements.
- Prompt Error Identification and Resolution: Identifying and correcting errors promptly is essential. Establishing a clear strategy for error correction, including who is responsible and the steps they should take, ensures swift resolution and maintains the integrity of financial records.
- Secure and Organized Source Documentation: Keeping source documents well-organized and secure facilitates easier access during the reconciliation process. Utilizing automation software can enhance this organization, providing secure storage and integration with existing data systems for comprehensive access to financial data.
- Comprehensive Documentation of the Process: Documenting the reconciliation process thoroughly is not only a requirement for audits but also supports internal control and clarity. This documentation should outline the reconciliation steps, responsible parties, timing, and procedures, ideally utilizing visual aids like flowcharts for better understanding.
By implementing these best practices, businesses can improve the reliability of their financial reconciliation process, ensuring accurate financial statements and facilitating smoother audit experiences.
Looking out for a Reconciliation Software?
Check out Nanonets Reconciliation where you can easily integrate Nanonets with your existing tools to instantly match your books and identify discrepancies.
How Nanonets Can 10x Financial Reconciliation
Traditional financial reconciliation processes often involve manual data entry, time-consuming document review, and the potential for human errors. However, with the advent of advanced automation technology like Nanonets, with its AI-driven Optical Character Recognition (OCR) features, businesses can streamline and accelerate their financial reconciliation efforts exponentially.
- Automated Data Extraction: Nanonets offers advanced OCR capabilities, allowing businesses to automatically extract data from various financial documents, including invoices, receipts, bank statements, and more. This eliminates the need for manual data entry and significantly reduces the time and effort required to gather and input financial information.
- Intelligent Document Processing: Nanonets also utilizes machine learning algorithms to intelligently process financial documents, categorize transactions, and identify discrepancies. By analyzing patterns and trends in financial data, Nanonets can flag potential errors or inconsistencies, allowing finance teams to focus their attention on resolving issues rather than sifting through mountains of paperwork.
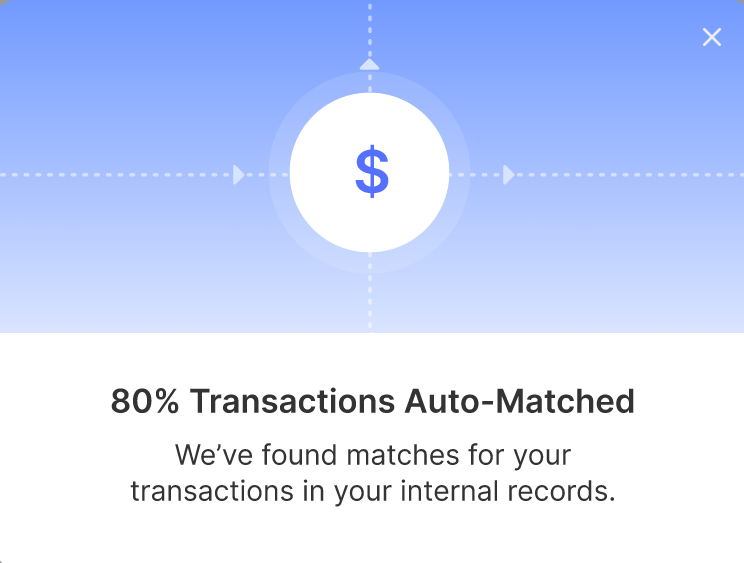
- Real-time Reconciliation: With Nanonets, financial reconciliation becomes a real-time process rather than a time-consuming monthly or quarterly task. By continuously scanning and analyzing financial data, Nanonets can identify discrepancies as soon as they occur, allowing businesses to take immediate action to resolve issues and maintain accurate financial records.
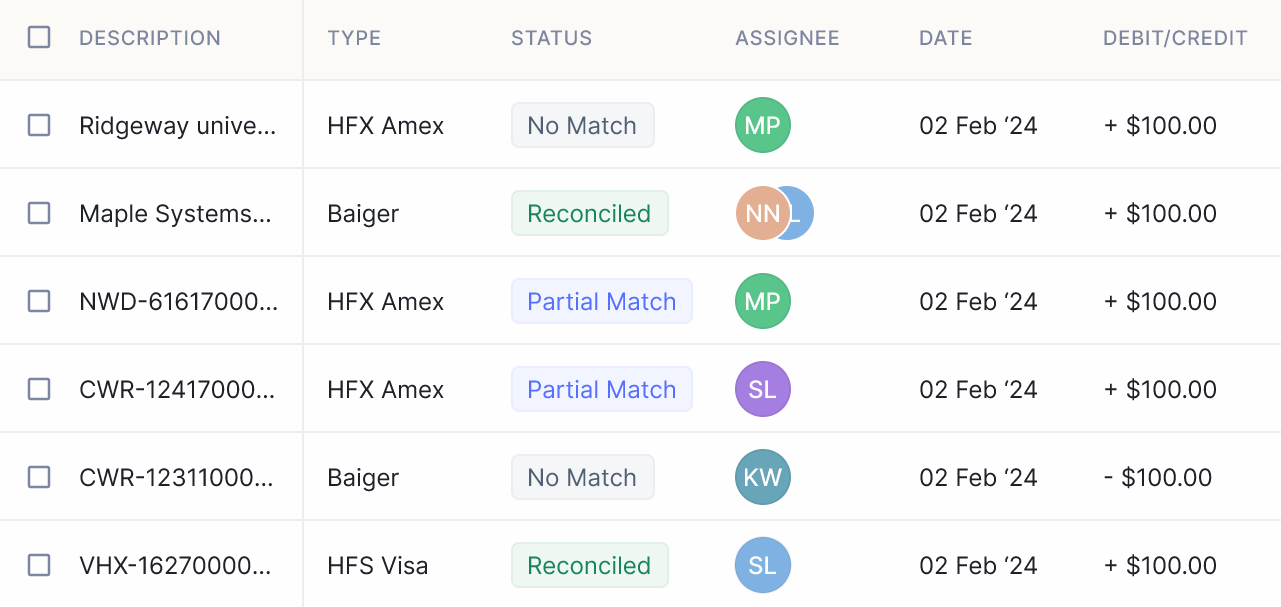
- Scalability and Flexibility: Nanonets is highly scalable and can adapt to the evolving needs of businesses of all sizes. Whether you're a small startup or a large enterprise, Nanonets can handle large volumes of financial data with ease, ensuring consistent and reliable results across your organization.

- Integration with Existing Systems: Nanonets seamlessly integrates with existing accounting software and ERP systems, allowing businesses to leverage their existing infrastructure while benefiting from the advanced capabilities of automation technology. This ensures a smooth transition to automated financial reconciliation processes without disrupting existing workflows.
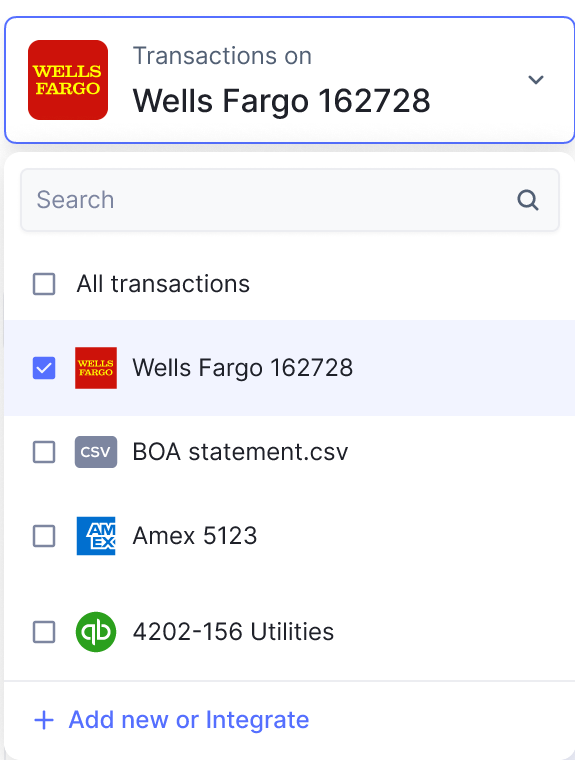
Overall, Nanonets empowers businesses to streamline their financial reconciliation efforts, reduce manual workload, minimize errors, and ensure compliance with regulatory requirements. By leveraging the power of automation, businesses can achieve greater efficiency, accuracy, and transparency in their financial operations, ultimately driving better business outcomes.
Conclusion
In conclusion, financial reconciliation is a critical process for businesses to ensure the accuracy, reliability, and integrity of their financial records. By comparing and aligning financial data from various sources, businesses can identify discrepancies, errors, and inconsistencies, allowing them to make informed decisions and maintain compliance with regulatory requirements.
With the advancements in automation technology, such as Nanonets, financial reconciliation has become more efficient, accurate, and streamlined than ever before. By leveraging automation tools, businesses can automate data extraction, matching, and reporting tasks, reducing manual workload, minimizing errors, and ensuring real-time visibility into their financial operations.
In today's fast-paced business environment, adopting automation technology for financial reconciliation is no longer a luxury but a necessity. Businesses that embrace automation can gain a competitive edge, drive operational efficiency, and achieve better business outcomes in the long run.
FAQs
What is financial reconciliation?
Financial reconciliation is the process of comparing financial records to ensure that they are accurate and reliable. It involves aligning transactions, balances, and other financial data from various sources to ensure consistency and completeness.
What are the main types of reconciliation?
The main types of reconciliation include bank reconciliation, balance sheet reconciliation, intercompany reconciliation, revenue reconciliation, and expense reconciliation. Each type focuses on different aspects of financial data and serves specific purposes in financial management.
Why is financial reconciliation important?
Financial reconciliation is important to ensure the accuracy and reliability of financial records. It helps businesses identify discrepancies, errors, and inconsistencies in their financial data, enabling them to make informed decisions, maintain compliance with regulatory requirements, and build trust with stakeholders.