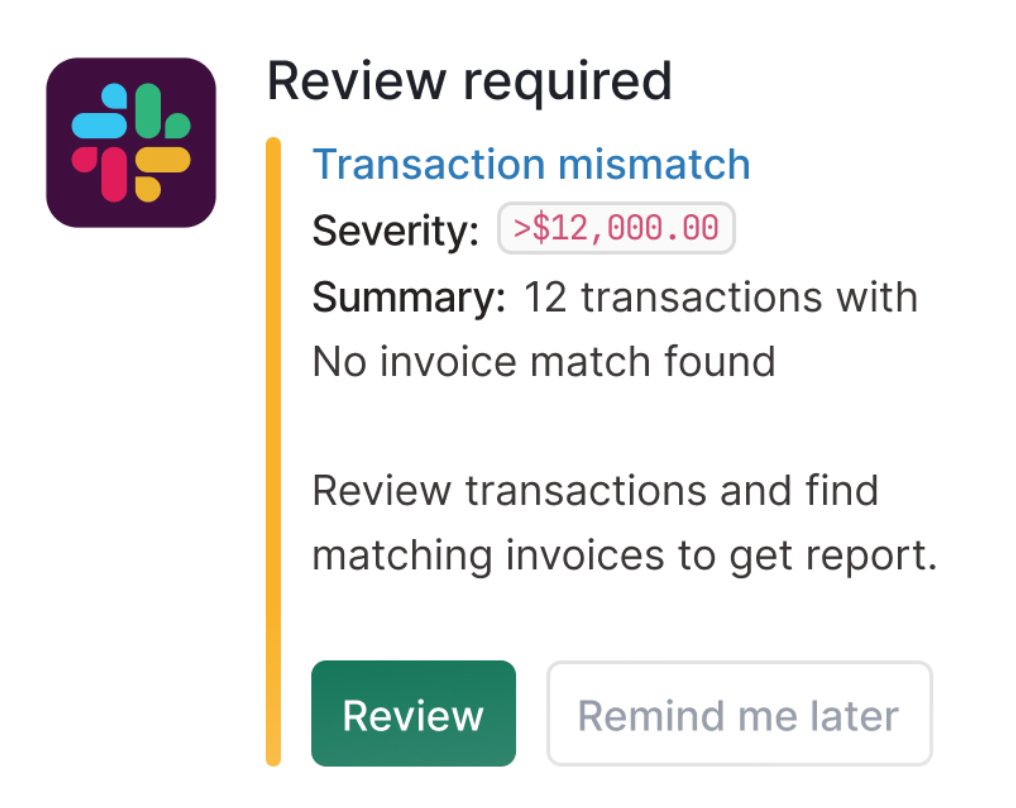
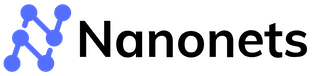Payment reconciliation: What is it, and how can your business do it efficiently?
Efficient payment reconciliation is a vital aspect of financial management for businesses of all sizes. As transactions flow in and out, reconciliation processes are crucial to ensure accuracy, identify discrepancies, and maintain a clear financial picture.
Payment reconciliation helps highlight data entry errors, duplicate payments, unpaid invoices, and other issues that could warrant further investigation.
In this article, we will learn what payment reconciliation is, how it works, and why your company needs to conduct them regularly. We will also highlight the benefits of automated reconciling of payments and how Nanonets can assist businesses in achieving seamless and accurate reconciliation processes .
What is payment reconciliation?
Payment reconciliation is a financial procedure that verifies transaction records by comparing them with bank statements, ensuring accuracy and consistency between internal financial records and actual transactions.
A payment reconciliation involves cross-checking bank statements with book-keeping records such as invoices, receipts, and other financial documents.

For example, let's consider a scenario where a company receives payments from multiple customers for its products or services. Reconciling payments involves verifying whether the payments received in the company's bank account match the corresponding invoices or payment records in the company's financial system. This process helps identify any missing or unmatched payments, duplicate transactions, or other errors that may impact the veracity of the financial records.
Why is payment reconciliation crucial for businesses?
Payment reconciliations are necessary to maintain financial accuracy, and regulatory compliance and keep a business’s operations running well. If there are any accounting errors, payment reconciliations help detect them, preventing unnecessary consequences.
One of the reasons to conduct payment reconciliations is to have an accurate understanding of a company’s financial health. Businesses thrive on being prepared for unforeseen circumstances, yet without accurate financial foresight, even the most well-thought-out strategies could unravel.
There are several consequences to inaccurate or missing payment reconciliations. It can lead to audit issues, potential internal fraud, vendor disputes, taxation problems, wasted resources, and even reputational damage.
Payment reconciliations might not be a top priority, but their absence will affect a business. They are the backbone of informed decision-making and financial stability and provide the necessary clarity to navigate intricate business uncertainties.
How does payment reconciliation work?
Payment reconciliations can be conducted for a business's internal and external cashflows.
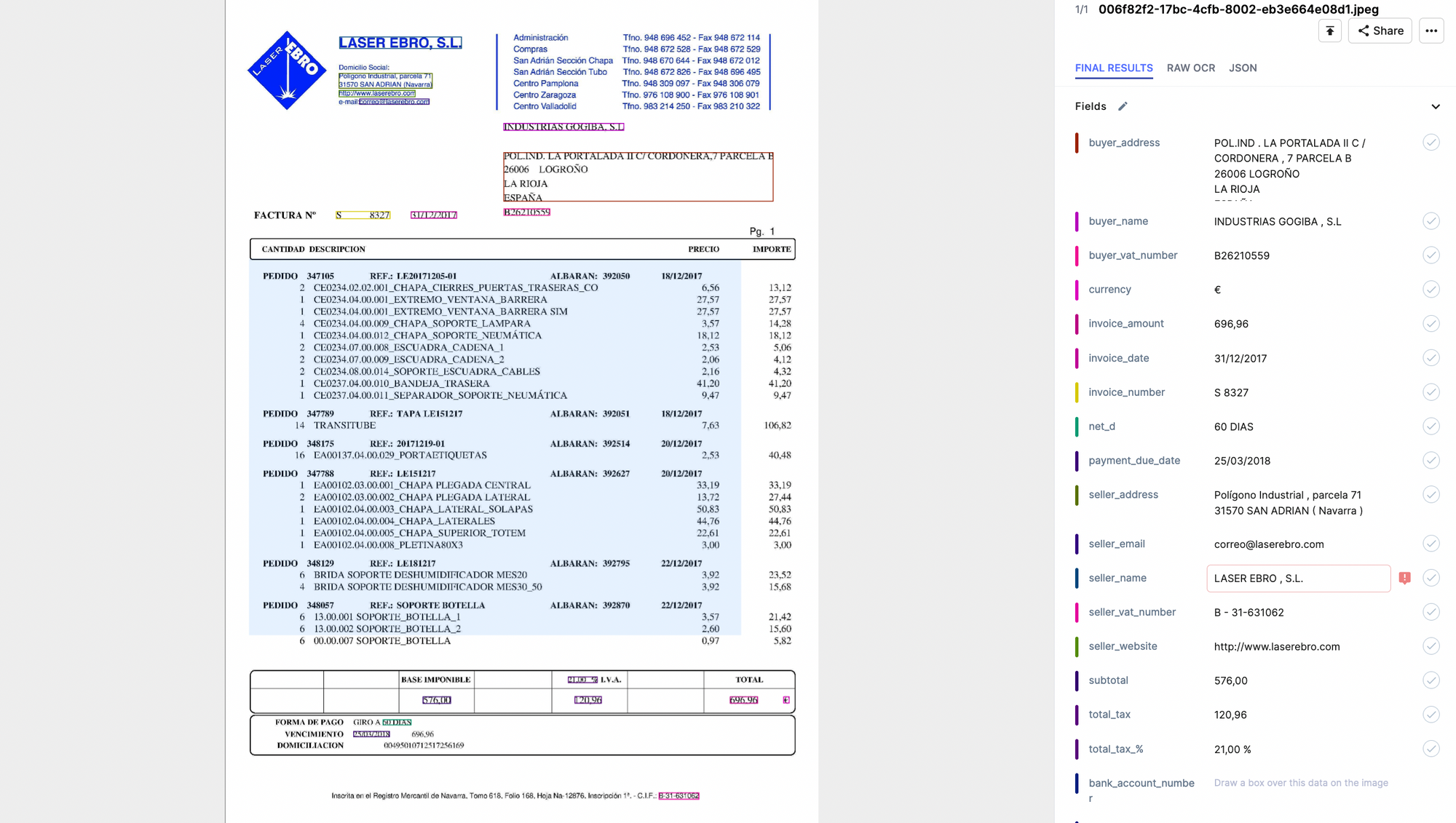
For both, there are a few common steps to follow:
- Gather data: The first step is to collect all relevant records to reconcile a payment. These include bank statements, accounting software records, invoices, receipts, and other relevant transaction records.
- Compare records: Once all documents relevant to a transaction are collected, compare and match the payment across different sources. Cross-reference transaction dates, amounts, payees, and reference numbers.
- Reconcile the accounts: If there are any discrepancies, determine their source(s) and make the necessary corrections to ensure accurate recording of payments.
- Validate and finalize reconciliation: Once the above is done, finalize the reconciliation process. Internal records should now accurately reflect the financial statements.
It is essential to perform payment reconciliations regularly, monthly or quarterly, to ensure that financial records remain accurate and up-to-date.
Payment reconciliation best practices
Every business can conduct payment reconciliations most suited to their requirements. When going about the process, there are a few best practices:
- Create and maintain a reconciliation schedule: Whether you perform payment reconciliations monthly or quarterly, create calendar events so you achieve them without fail. Frequent reconciliations help break the process down and identify discrepancies quickly.
- Consider using automation: Accounting software or financial management systems that offer automated reconciliation features can help match transactions, flag discrepancies, and streamline the process. This helps save time and reduce human error.
- Assign duties: Separate the employees' roles in initiating, approving, and reconciling payments. This helps prevent fraud and ensures that no single person has complete control over the entire payment process.
- Document the process: Create clear, step-by-step documentation outlining your payment reconciliation procedures. This documentation serves as a reference for employees, ensures consistency, and aids in training new team members.
- Review for patterns: Regularly review reconciliation reports for any patterns of errors or discrepancies. Identifying recurring issues allows you to implement corrective actions to prevent them from happening again.
A practical payment reconciliation process can reduce confusion and help establish clear goals for all departments involved.
Looking out for a Reconciliation Software?
Check out Nanonets Reconciliation where you can easily integrate Nanonets with your existing tools to instantly match your books and identify discrepancies.
Challenges of manual payment reconciliation
According to a PWC report, 30 percent of a finance team’s time may be spent on manual reconciliation. Even in top-quartile companies, analysts spend 40 percent of their time gathering data, not analyzing it!
Manual payment reconciliation is arduous because of the high data volume and complex payment structures. Businesses receive numerous payments from various sources, often in different currencies, via various payment methods. Thus, the data's sheer volume and complexity make it prone to errors and delays.
Further, manual data entry introduces the risk of human errors and inconsistencies. Even with meticulous attention to detail, manual reconciliation increases the likelihood of data entry mistakes, transposition errors, or missing transactions. These errors can result in inaccurate financial records, payment discrepancies, and potential financial losses.
The manual matching, cross-referencing, and investigation of payment records can take hours or even days, especially for businesses with many transactions. The time spent on manual reconciliation could be better utilized on more value-added activities, such as analyzing financial data or improving customer relationships.
Further, manual reconciliation often lacks real-time visibility into payment status and updates. Without timely information, businesses may experience delays in identifying and addressing discrepancies. This can result in missed opportunities, delayed decision-making, and potential disruptions in cash flow management.
As businesses grow and the volume of transactions increases, manual reconciliation becomes increasingly challenging to scale.
Fortunately, automation can offer significant benefits to the payment reconciliation process. In the next section, we will explore how automation can streamline the payment reconciliation process, its benefits, and how it can be achieved.
Types of Payment Reconciliation
Payment reconciliation, sometimes referred to as “Book Keeping” has two components:
- Inward Reconciliation: Inward reconciliation involves the internal processing of financial transactions within a business. This includes collecting and recording payments, invoices, and billing information. Whether it's managing receipts manually, using financial software, or maintaining spreadsheets, the goal remains the same - to accurately track incoming payments and financial activities. However, with a high volume of transactions, there's a risk of being overwhelmed by paperwork. Efficient systems and processes help streamline this component, minimizing errors and optimizing efficiency.
- Outward Reconciliation: Outward reconciliation is the process of comparing internal records with external statements provided by banks or financial institutions. These statements typically include transaction details, balances, and other financial activities. The aim here is to ensure that the transactions recorded internally align with those reflected in the bank statements. Any discrepancies or inconsistencies discovered during this comparison need to be investigated thoroughly to identify the root causes. This component plays a crucial role in maintaining financial accuracy and compliance with banking regulations.
There are many types of payment reconciliation.
- Bank Reconciliation: Bank reconciliation is a process where businesses ensure their internal cash records match the closing balance on their bank statement. This involves crosschecking deposits, disbursements, and account fees to catch any discrepancies. It's crucial for avoiding missed payments, hidden fees, and maintaining accurate financial records.
- Cash Reconciliation: Cash reconciliation is essential for businesses to monitor their cash flow effectively. It involves comparing the company's ledger with actual cash transactions to ensure every dollar is properly accounted for. This becomes increasingly challenging with high transaction volumes.
- Credit Card Reconciliation: Credit card reconciliation entails verifying that the records in the credit card statement align with the company's general ledger. Any disparities discovered during this process require investigation to determine the cause. This type of reconciliation ensures accuracy in tracking digital transactions and prevents financial discrepancies.
- Digital Wallet Reconciliation: As digital transactions become more prevalent, reconciling digital wallets is crucial. This process involves verifying transactions recorded in digital wallet statements against the company's financial records. It's about ensuring accuracy in tracking digital payments and maintaining financial integrity in the digital realm.
- Accounts Receivable Reconciliation: Accounts receivable reconciliation involves comparing customer payments and credit notes with the invoices issued by the business. This process ensures that records of customer payments are accurate and complete. It allows businesses to identify any discrepancies, such as underpayments or overpayments, and take appropriate action to resolve them.
- Accounts Payable Reconciliation: Accounts payable reconciliation involves matching supplier invoices, credit notes, and payments made by the business. This process ensures that the amounts owed to suppliers are accurate and that payments are made on time. By reconciling accounts payable records, businesses can verify the accuracy of their financial obligations and maintain positive relationships with suppliers.
- Global Currencies Reconciliation: Businesses dealing with multiple currencies must reconcile transactions conducted in different currencies with their financial records. This ensures accuracy in financial reporting, especially amidst currency fluctuations. It's essential for businesses operating on a global scale to maintain accurate records across various currencies.
Benefits of Automated Payment Reconciliation
Automated payment reconciliation offers a multitude of advantages for businesses seeking to streamline their financial processes and enhance efficiency. Here are some key benefits:
- Time-Saving: Automation significantly reduces the time and effort required for payment reconciliation tasks. According to McKinsey, workflow automation has the potential to save 30% of time for approximately 60% of employees. By automatically matching transactions and identifying discrepancies, businesses can expedite the reconciliation process and free up valuable resources for other strategic activities.
- Accuracy and Error Reduction: Automated reconciliation systems are designed to minimize human error and ensure accuracy in financial records. By leveraging advanced algorithms and matching criteria, these systems can identify discrepancies more effectively than manual methods, reducing the risk of misallocation or oversight.
- Real-Time Visibility: Automated reconciliation provides businesses with real-time visibility into their financial transactions. This enables stakeholders to access up-to-date information on payment statuses, outstanding balances, and transaction trends, empowering them to make informed decisions.
- Fraud Prevention: Automated reconciliation systems play a crucial role in fraud prevention by detecting anomalies and irregularities in financial transactions. Through advanced data analysis and pattern recognition, these systems can identify potential fraudulent activities such as unauthorized payments, duplicate transactions, or unusual spending patterns. By flagging suspicious transactions in real time, automated reconciliation helps businesses mitigate the risk of financial fraud and protect their assets. This proactive approach to fraud prevention enhances financial security and safeguards the integrity of business operations.
- Enhanced Compliance and Control: Automated reconciliation systems help businesses maintain compliance with regulatory requirements and internal policies. By enforcing standardized reconciliation procedures and documentation, these systems ensure consistency and transparency in financial reporting, reducing the risk of compliance violations.
- Cost Savings: While there may be initial investment costs associated with implementing automated reconciliation systems, the long-term benefits often outweigh the expenses. In the simplest case, it saves printing and paper costs. Gartner estimates that total print costs—from hardware to maintenance to supplies—eat up 1-3% of a company’s overall revenue. Furthermore, By improving efficiency, reducing errors, and minimizing the need for manual labor, businesses can achieve significant cost savings over time.
- Scalability and Adaptability: Automated reconciliation systems are highly scalable and adaptable to the evolving needs of businesses. Whether handling a small volume of transactions or managing complex payment flows across multiple channels, these systems can adjust to accommodate changing requirements and transaction volumes.
- Improved Decision-Making: By providing accurate and timely insights into financial data, automated reconciliation enables businesses to make better-informed decisions. Whether optimizing cash flow management, identifying opportunities for cost savings, or mitigating financial risks, access to reliable reconciliation data is essential for strategic decision-making.
Risks of Automated Payment Reconciliation
While Paul Ehrlich's assertion that “to err is human, but to really foul things up requires a computer,” may have exaggerated the risks, it's prudent to acknowledge that there are still a a few associated with automated payment reconciliation.
- Data Inaccuracy: Automated reconciliation systems rely on data inputs from various sources. Errors or inconsistencies in these inputs can lead to inaccuracies in reconciliation results; after all, what is sown is reaped. Whether it's incorrect transaction data, system glitches, or integration issues, data inaccuracies can undermine the reliability of automated reconciliation processes.
- Operational Disruptions: Automated reconciliation systems are susceptible to operational disruptions, such as software failures, system downtime, or integration issues. These disruptions can disrupt business operations, delay financial reporting, or result in processing errors, impacting overall efficiency and productivity.
- Cybersecurity Threats: Automated reconciliation systems are attractive targets for cybercriminals seeking to exploit vulnerabilities in software or gain unauthorized access to sensitive financial data. Cybersecurity threats, such as malware attacks, phishing scams, or data breaches, pose a significant risk to the integrity and security of automated reconciliation processes.
- Dependency on Technology: Dependency on automated technology for payment reconciliation can pose risks associated with system failures, software bugs, or technical glitches. Businesses may become overly reliant on technology, leading to complacency in manual oversight or control mechanisms.
- Cost of Implementation and Maintenance: Implementing and maintaining automated reconciliation systems require significant investment in technology infrastructure, software licenses, and ongoing support and maintenance. Businesses must carefully weigh the costs and benefits of automation to ensure a positive return on investment.
- Compliance Violations: Non-compliance with regulatory requirements or internal policies poses a significant risk in automated payment reconciliation. Inadequate controls or oversight can result in compliance violations, leading to legal consequences, fines, or reputational damage for the organization.
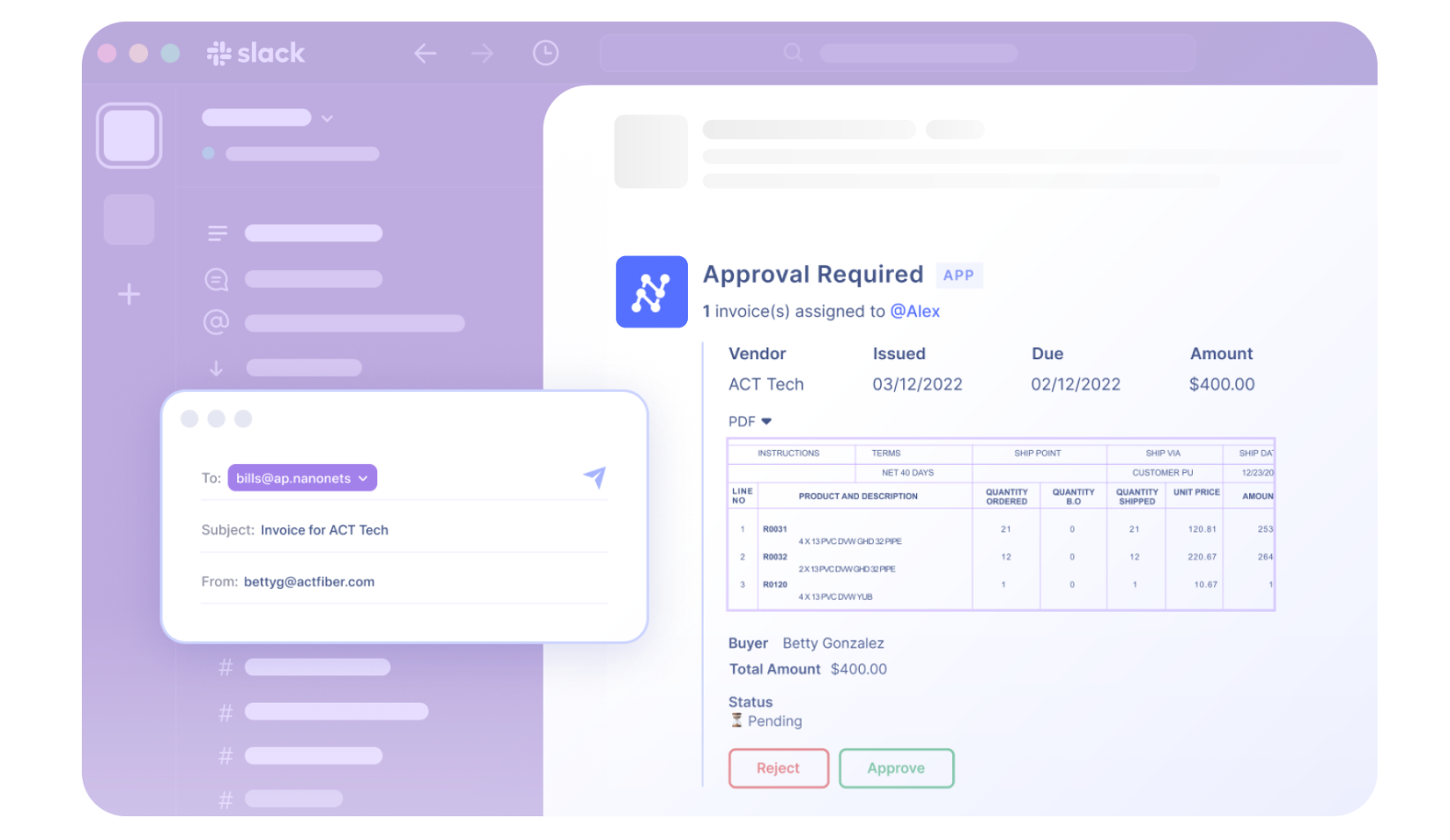
Automate payment reconciliation with Nanonets
Nanonets is a leading provider of AI-powered automation solutions to streamline payment reconciliation. With its advanced machine learning algorithms, Nanonets can automate the matching and verifying of payment data, ensuring accuracy and efficiency.
Nanonets is a top choice for Payment reconciliation software. Here's why:
- Advanced Automation: Nanonets harnesses the power of AI and machine learning to automate the reconciliation process efficiently. Its auto-extraction capabilities ensure seamless data retrieval from various sources, while AI-driven matching algorithms accurately reconcile transactions, reducing manual effort and errors.
- Versatile Integration: Nanonets seamlessly integrates with existing accounting systems and data sources, enabling smooth data flow and synchronization. Whether it's ACH payment processing, accounting integration, or API connections, Nanonets offers versatile integration options to fit your organization's needs.
- Ease of Use: Nanonets boasts an intuitive interface and user-friendly design, making it easy for finance professionals to navigate and utilize its features effectively. From customizable workflows to collaborative tools, Nanonets prioritizes simplicity without compromising functionality.
- Scalability: Whether you're a small startup or a large enterprise, Nanonets scales effortlessly to accommodate your organization's growth. Its flexible pricing plans and modular features ensure scalability without overburdening your budget or IT infrastructure.

- Accuracy and Reliability: Nanonets prioritizes accuracy and reliability in balance sheet reconciliation. With built-in audit trails, validation checks, and compliance management features, Nanonets ensures data integrity and regulatory compliance, giving you peace of mind.
- Exceptional Customer Support: Nanonets is backed by a dedicated customer support team committed to providing timely assistance and resolving any issues promptly. From implementation to ongoing support, Nanonets ensures a smooth and seamless experience for its users.
- Positive User Feedback: User reviews and ratings on platforms like Capterra consistently highlight Nanonets' effectiveness, ease of use, and value for money. With high scores across various categories, Nanonets earns the trust and satisfaction of its users.

Nanonets offers a user-friendly interface that allows businesses to train the system to recognize payment patterns, match payments with invoices, and flag exceptions for review. Its intelligent automation capabilities enable businesses to achieve higher levels of accuracy, streamline the reconciliation workflow, and improve financial control.
Nanonets' AI-powered automation solutions offer a robust platform to streamline the payment reconciliation process, improve efficiency, and ensure reliable financial records. By leveraging the power of automation, businesses can optimize their payment reconciliation efforts and focus on strategic financial management.
FAQs
What is payment reconciliation?
Payment reconciliation is an important accounting process that helps to ensure the accuracy of a company's financial records. It involves comparing the company's internal records of payments made and received to the corresponding entries on its bank statements.
What are the 3 main types of reconciliation?
Bank reconciliation, vendor reconciliation, and customer reconciliation.
Why should you automate payment reconciliation?
Automating payment reconciliation can save businesses a significant amount of time and effort. It can also help to reduce the risk of errors, which can lead to financial losses.